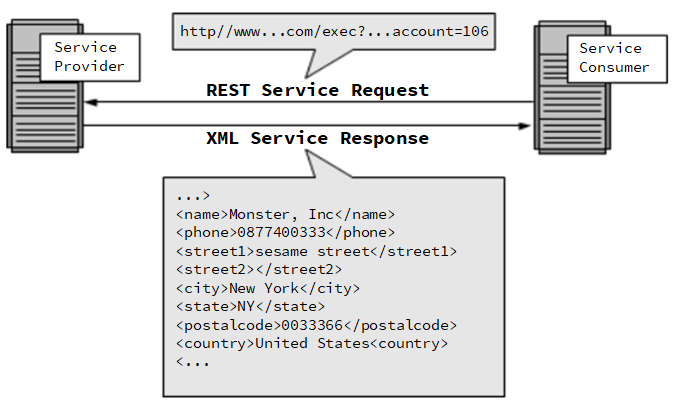
RESTful Service
Representational State Transfer (REST) is a style of architecture based on a set of principles that describe how networked resources are defined and addressed. These principles were first described in 2000 by Roy Fielding as part of his doctoral dissertation. REST is an alternative to SOAP and JavaScript Object Notation (JSON).
It is important to note that REST is a style of software architecture as opposed to a set of standards. As a result, such applications or architectures are sometimes referred to as RESTful or REST-style applications or architectures. REST has proved to be a popular choice for implementing Web Services. For example, the books suggested at the bottom of many of these article pages are dynamically generated, in part, using a REST architecture. It is one of the options for Amazon Web Services
An application or architecture considered RESTful or REST-style is characterized by:
1.State and functionality are divided into distributed resources 2.Every resource is uniquely addressable using a uniform and minimal set of commands (typically using HTTP commands of GET, POST, PUT, or DELETE over the Internet) 3.The protocol is client/server, stateless, layered, and supports caching